HOOPS AI - Minimal ETL Demo
This notebook demonstrates the core features of the HOOPS AI data engineering workflows:
Key Components
Schema-Based Dataset Organization: Define structured data schemas for consistent data merging
Parallel Task Decorators: Simplify CAD processing with type-safe task definitions
Generic Flow Orchestration: Automatically handle task dependencies and data flow
Automatic Dataset Merging: Process multiple files into a unified dataset structure
Integrated Exploration Tools: Analyze and prepare data for ML workflows
The framework automatically generates visualization assets and stream cache data to support downstream applications.
[1]:
import hoops_ai
import os
# Note: License is also set in cad_tasks.py for worker processes
# This is only for the parent process (optional but good practice)
hoops_ai.set_license(hoops_ai.use_test_license(), validate=False)
ℹ️ Using TEST LICENSE (expires February 8th, 2026 - 9 days remaining)
For production use, obtain your own license from Tech Soft 3D
HOOPS AI version : 1.0.0-b2dev12
Import Dependencies
The HOOPS AI framework provides several key modules:
flowmanager: Core orchestration engine with task decoratorscadaccess: CAD file loading and model access utilitiesstorage: Data persistence and retrieval componentsdataset: Tools for exploring and preparing merged datasets
[2]:
import os
import pathlib
from typing import Tuple, List
# Import the flow builder framework from the library
import hoops_ai
from hoops_ai.flowmanager import flowtask
from hoops_ai.cadaccess import HOOPSLoader, HOOPSTools
from hoops_ai.cadencoder import BrepEncoder
from hoops_ai.dataset import DatasetExplorer
from hoops_ai.storage import DataStorage, CADFileRetriever, LocalStorageProvider
from hoops_ai.storage.datasetstorage.schema_builder import SchemaBuilder
Configuration Setup
Define input and output paths for CAD processing:
Input directory containing source CAD files
Output directory for processed results
Source directory with specific CAD file formats
The framework will automatically organize outputs into structured directories.
[3]:
# Configuration - Using simpler paths
nb_dir = pathlib.Path.cwd()
datasources_dir = nb_dir.parent.joinpath("packages","cadfiles","cadsynth100","step")
if not datasources_dir.exists():
print("Data source directory does not exist. Please check the path.")
exit(-1)
flows_outputdir = nb_dir.joinpath("out")
Schema Definition - The Foundation of Dataset Organization
The SchemaBuilder defines a structured blueprint for how CAD data should be organized:
Domain & Version: Namespace and versioning for schema tracking
Groups: Logical data categories (e.g., “machining”, “faces”, “edges”)
Arrays: Typed data containers with defined dimensions
Metadata Routing: Rules for routing metadata to appropriate storage
Schemas ensure consistent data organization across all processed files, enabling automatic merging and exploration.
[4]:
# Schema is now defined in cad_tasks.py for ProcessPoolExecutor compatibility
# Import it from there to view or customize
from scripts.cad_tasks import cad_schema
print(cad_schema)
ℹ️ Using TEST LICENSE (expires February 8th, 2026 - 9 days remaining)
For production use, obtain your own license from Tech Soft 3D
HOOPS AI version : 1.0.0-b2dev12
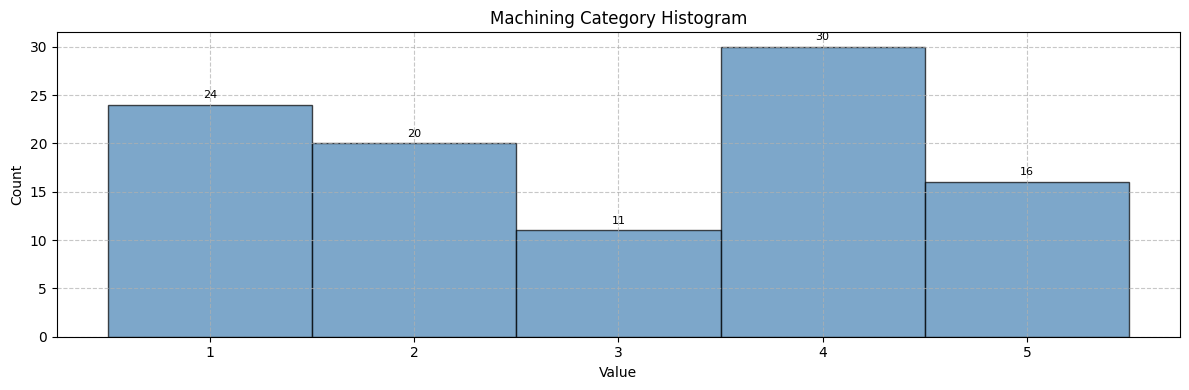
{'version': '1.0', 'domain': 'Manufacturing_Analysis', 'groups': {'machining': {'primary_dimension': 'part', 'arrays': {'machining_category': {'dims': ['part'], 'dtype': 'int32', 'description': 'Machining complexity category (1-5)'}, 'material_type': {'dims': ['part'], 'dtype': 'int32', 'description': 'Material type (1-5)'}, 'estimated_machining_time': {'dims': ['part'], 'dtype': 'float32', 'description': 'Estimated machining time in hours'}}, 'description': 'Manufacturing and machining classification data'}}, 'description': 'Minimal schema for manufacturing classification', 'metadata': {'metadata': {'file_level': {}, 'categorical': {'material_type_description': {'dtype': 'str', 'required': False, 'description': 'Material classification'}}, 'routing_rules': {'file_level_patterns': [], 'categorical_patterns': ['material_type_description', 'category', 'type'], 'default_numeric': 'file_level', 'default_categorical': 'categorical', 'default_string': 'categorical'}}}}
[ ]:
[5]:
# Import task functions from external module for ProcessPoolExecutor compatibility
from scripts.cad_tasks import gather_files, encode_manufacturing_data
[6]:
from display_utils import display_task_source
display_task_source(gather_files, "gather_files")
gather_files
@flowtask.extract(
name="gather cad files",
inputs=["cad_datasources"],
outputs=["cad_dataset"],
parallel_execution=True
)
def gather_files(source: str) -> List[str]:
# Use simple glob pattern matching for ProcessPoolExecutor compatibility
patterns = ["*.stp", "*.step", "*.iges", "*.igs"]
source_files = []
for pattern in patterns:
search_path = os.path.join(source, pattern)
files = glob.glob(search_path)
source_files.extend(files)
print(f"Found {len(source_files)} CAD files in {source}")
return source_files
[7]:
display_task_source(encode_manufacturing_data, "encode_manufacturing_data")
encode_manufacturing_data
@flowtask.transform(
name="Manufacturing data encoding",
inputs=["cad_dataset"],
outputs=["cad_files_encoded"],
parallel_execution=True
)
def encode_manufacturing_data(cad_file: str, cad_loader: HOOPSLoader, storage: DataStorage) -> str:
# Load CAD model using the process-local HOOPSLoader
cad_model = cad_loader.create_from_file(cad_file)
# Set the schema for structured data organization
# Schema is defined at module level, so it's available in all worker processes
storage.set_schema(cad_schema)
# Prepare BREP for feature extraction
hoopstools = HOOPSTools()
hoopstools.adapt_brep(cad_model, None)
# Extract geometric features using BrepEncoder
brep_encoder = BrepEncoder(cad_model.get_brep(), storage)
# Topology & Graph
graph = brep_encoder.push_face_adjacency_graph()
extended_adj = brep_encoder.push_extended_adjacency()
neighbors_count = brep_encoder.push_face_neighbors_count()
edge_paths = brep_encoder.push_face_pair_edges_path(max_allow_edge_length=16)
# Geometric Indices & Attributes
face_attrs, face_types_dict = brep_encoder.push_face_attributes()
face_discretization = brep_encoder.push_face_discretization(pointsamples=100)
edge_attrs, edge_types_dict = brep_encoder.push_edge_attributes()
curve_grids = brep_encoder.push_curvegrid(ugrid=10)
# Face-Pair Histograms
distance_hists = brep_encoder.push_average_face_pair_distance_histograms(grid=10, num_bins=64)
angle_hists = brep_encoder.push_average_face_pair_angle_histograms(grid=10, num_bins=64)
# Generate manufacturing classification data
file_basename = os.path.basename(cad_file)
file_name = os.path.splitext(file_basename)[0]
# Set seed for reproducible results based on filename
random.seed(hash(file_basename) % 1000)
# Generate classification values
machining_category = random.randint(1, 5)
material_type = random.randint(1, 5)
estimated_time = random.uniform(0.5, 10.0)
# Material type descriptions
material_descriptions = ["Steel", "Aluminum", "Titanium", "Plastic", "Composite"]
# Save data using the OptStorage API (data_key format: "group/array_name")
storage.save_data("machining/machining_category", np.array([machining_category], dtype=np.int32))
storage.save_data("machining/material_type", np.array([material_type], dtype=np.int32))
storage.save_data("machining/estimated_machining_time", np.array([estimated_time], dtype=np.float32))
# Save categorical metadata (will be routed to .attribset)
storage.save_metadata("material_type_description", material_descriptions[material_type - 1])
# Save file-level metadata (will be routed to .infoset)
storage.save_metadata("Item", str(cad_file))
storage.save_metadata("Flow name", "minimal_manufacturing_flow")
# Compress the storage into a .data file
storage.compress_store()
return storage.get_file_path("")
Flow Orchestration and Automatic Dataset Generation
The hoops_ai.create_flow() function orchestrates the data flow execution. The tasks parameters can receive any function defined by the user. This is fully editable, you can write your OWN encoding logic.
[8]:
# Create and run the Data Flow
flow_name = "minimal_manufacturing_flow"
cad_flow = hoops_ai.create_flow(
name=flow_name,
tasks=[gather_files, encode_manufacturing_data], # Imported from cad_tasks.py
max_workers=6, # parallel running
flows_outputdir=str(flows_outputdir),
ml_task="Manufacturing Classification Demo",
auto_dataset_export=True, # Enable automatic dataset merging
debug=False, # Changed to False to enable parallel execution
export_visualization=True
)
# Run the flow to process all files
print("Starting flow execution with ProcessPoolExecutor...")
print("✓ Schema is defined in cad_tasks.py, available to all worker processes")
flow_output, output_dict, flow_file = cad_flow.process(inputs={'cad_datasources': [str(datasources_dir)]})
# Display results
print("\n" + "="*70)
print("FLOW EXECUTION COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY")
print("="*70)
print(f"\nDataset files created:")
print(f" Main dataset: {output_dict.get('flow_data', 'N/A')}")
print(f" Info dataset: {output_dict.get('flow_info', 'N/A')}")
print(f" Attributes: {output_dict.get('flow_attributes', 'N/A')}")
print(f" Flow file: {flow_file}")
print(f"\nTotal processing time: {output_dict.get('Duration [seconds]', {}).get('total', 0):.2f} seconds")
print(f"Files processed: {output_dict.get('file_count', 0)}")
Starting flow execution with ProcessPoolExecutor...
✓ Schema is defined in cad_tasks.py, available to all worker processes
|INFO| FLOW | ######### Flow 'minimal_manufacturing_flow' start #######
|WARNING| FLOW | Cleaning up existing flow directory: C:\Users\LuisSalazar\Documents\MAIN\MLProject\repo\HOOPS-AI-tutorials\notebooks\out\flows\minimal_manufacturing_flow
|WARNING| FLOW | Removing all previous outputs for flow 'minimal_manufacturing_flow' to avoid build conflicts.
|INFO| FLOW | Flow directory successfully cleaned and recreated: C:\Users\LuisSalazar\Documents\MAIN\MLProject\repo\HOOPS-AI-tutorials\notebooks\out\flows\minimal_manufacturing_flow
|INFO| FLOW |
Flow Execution Summary
|INFO| FLOW | ==================================================
|INFO| FLOW | Task 1: gather cad files
|INFO| FLOW | Inputs : cad_datasources
|INFO| FLOW | Outputs: cad_dataset
|INFO| FLOW | Task 2: Manufacturing data encoding
|INFO| FLOW | Inputs : cad_dataset
|INFO| FLOW | Outputs: cad_files_encoded
|INFO| FLOW | Task 3: AutoDatasetExportTask
|INFO| FLOW | Inputs : cad_files_encoded
|INFO| FLOW | Outputs: encoded_dataset, encoded_dataset_info, encoded_dataset_attribs
|INFO| FLOW |
Task Dependencies:
|INFO| FLOW | gather cad files has no dependencies.
|INFO| FLOW | gather cad files --> Manufacturing data encoding
|INFO| FLOW | Manufacturing data encoding --> AutoDatasetExportTask
|INFO| FLOW | ==================================================
|INFO| FLOW | Executing ParallelTask 'gather cad files' with 1 items.
|INFO| FLOW | Executing ParallelTask 'Manufacturing data encoding' with 101 items.
|INFO| FLOW | Executing SequentialTask 'AutoDatasetExportTask'.
[DatasetMerger] Saved schema with 5 groups to metadata.json
|INFO| FLOW | Auto dataset export completed in 30.61 seconds
Sequential Task end=====================
|INFO| FLOW | Time taken: 266.06 seconds
|INFO| FLOW | ######### Flow 'minimal_manufacturing_flow' end ######
======================================================================
FLOW EXECUTION COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY
======================================================================
Dataset files created:
Main dataset: C:\Users\LuisSalazar\Documents\MAIN\MLProject\repo\HOOPS-AI-tutorials\notebooks\out\flows\minimal_manufacturing_flow\minimal_manufacturing_flow.dataset
Info dataset: C:\Users\LuisSalazar\Documents\MAIN\MLProject\repo\HOOPS-AI-tutorials\notebooks\out\flows\minimal_manufacturing_flow\minimal_manufacturing_flow.infoset
Attributes: C:\Users\LuisSalazar\Documents\MAIN\MLProject\repo\HOOPS-AI-tutorials\notebooks\out\flows\minimal_manufacturing_flow\minimal_manufacturing_flow.attribset
Flow file: C:\Users\LuisSalazar\Documents\MAIN\MLProject\repo\HOOPS-AI-tutorials\notebooks\out/flows/minimal_manufacturing_flow/minimal_manufacturing_flow.flow
Total processing time: 266.06 seconds
Files processed: 101
[ ]: