
HOOPS AI: Encoder Module
BrepEncoder
The BrepEncoder class is responsible for computing and persisting geometry and topology data from a B-rep. It provides methods (called “push” methods) that extract specific features from the model and if the DataStorage object is provided, it can storage it in a compressed optimal file. Very handy when working with large datasets.
[1]:
import hoops_ai
hoops_ai.set_license(hoops_ai.use_test_license(), validate = False)
ℹ️ Using TEST LICENSE (expires February 8th, 2026 - 9 days remaining)
For production use, obtain your own license from Tech Soft 3D
HOOPS AI version : 1.0.0-b2dev12
View your cad model in the notebook
[2]:
import pathlib
#TEST CAD FILE
cad_filename = pathlib.Path.cwd().parent.joinpath("packages", "cadfiles", "pn_verschr_r1.prt.1")
from hoops_ai.insights import CADViewer
import pathlib
output_dir = pathlib.Path.cwd().joinpath("out")
if not output_dir.exists():
os.makedirs(output_dir)
viewer = CADViewer(static_folder=output_dir)
viewer.load_cad_file(cad_filename)
[2]:
True
[3]:
viewer.show()
status = viewer.get_status()
print(f"Viewer is running on port: {status['port']}")
print(f"Viewer URL: {status['viewer_url']}")
Viewer is running on port: 8002
Viewer URL: http://127.0.0.1:8002
Initialize the HOOPSLoader and set the BRep options
[4]:
from hoops_ai.cadaccess import HOOPSLoader, HOOPSModel, HOOPSTools
[5]:
# open the cad file
cad_loader = HOOPSLoader()
cad_model = cad_loader.create_from_file(str(cad_filename))
# Adapt to extract BRep information
hoopstools = HOOPSTools()
hoopstools.adapt_brep(cad_model)
BRep data as numerical features for ML
[6]:
from hoops_ai.cadencoder import BrepEncoder
brep_encoder = BrepEncoder(cad_model.get_brep())
Encoding the Topology
push_face_adjacency_graph() -> nx.Graph
Builds and stores a face adjacency graph from the B-rep model. This graph represents the topology of the model where nodes are faces and edges connect adjacent faces.
[7]:
adj_graph = brep_encoder.push_face_adjacency_graph()
[8]:
import matplotlib_inline
matplotlib_inline.backend_inline.set_matplotlib_formats("retina")
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
pos = nx.kamada_kawai_layout(adj_graph)
nx.draw_networkx(adj_graph, pos, arrows=False) # draw nodes, edges, labels
plt.axis('off') # turn off axes for clarity
plt.show()
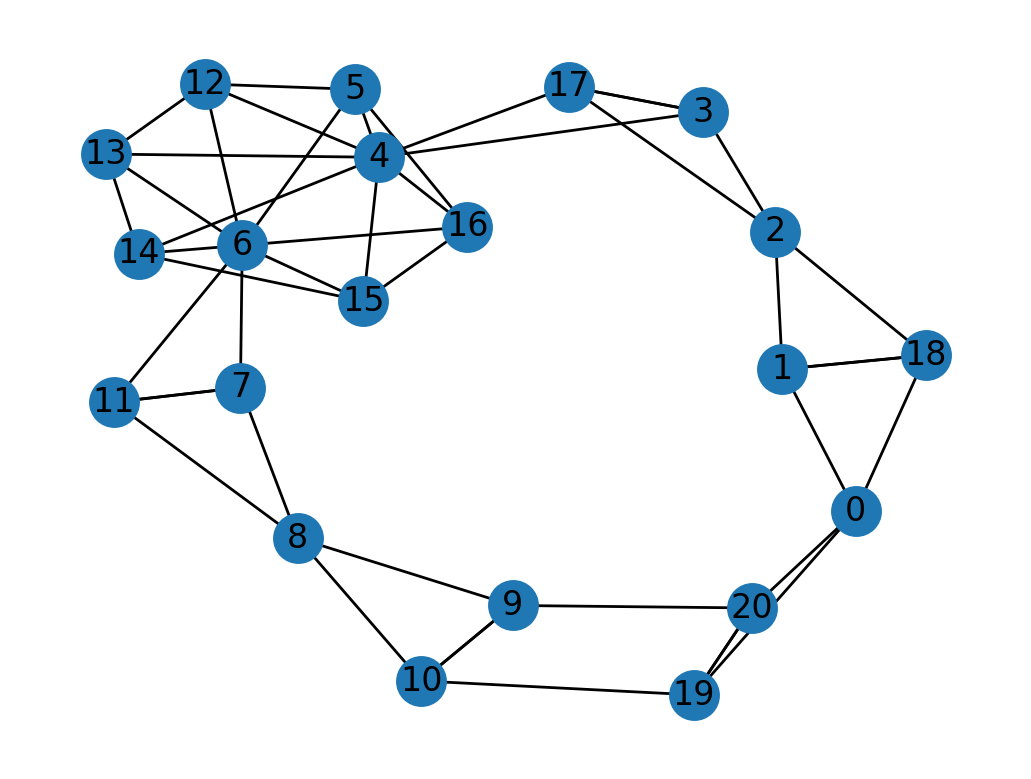
[9]:
face_index = 9
neighbor_faces = set(adj_graph.successors(face_index)) | set(adj_graph.predecessors(face_index))
print(neighbor_faces)
{8, 10, 20}
[10]:
viewer.set_face_color([9], [255,0,0])
[11]:
viewer.set_face_color(neighbor_faces, [155,155,0])
[12]:
viewer.clear_face_colors()
[15]:
# INTERACTIVE Get the face indices you selected interactively
selected_faces = viewer.get_selected_faces()
print(f"You selected {len(selected_faces)} faces: {selected_faces}")
You selected 2 faces: [2, 15]
[16]:
# Highlight selected faces with a custom green color
viewer.set_face_color(selected_faces, [150, 255, 100])
Utilities for quick visualization using repo scripts folder
[17]:
from scripts import helper_tutorials
[18]:
avg_distance = brep_encoder.push_average_face_pair_distance_histograms(10,5)
#print(avg_distance)
[19]:
helper_tutorials.plot_bar(avg_distance[15,10]) #[15,10]
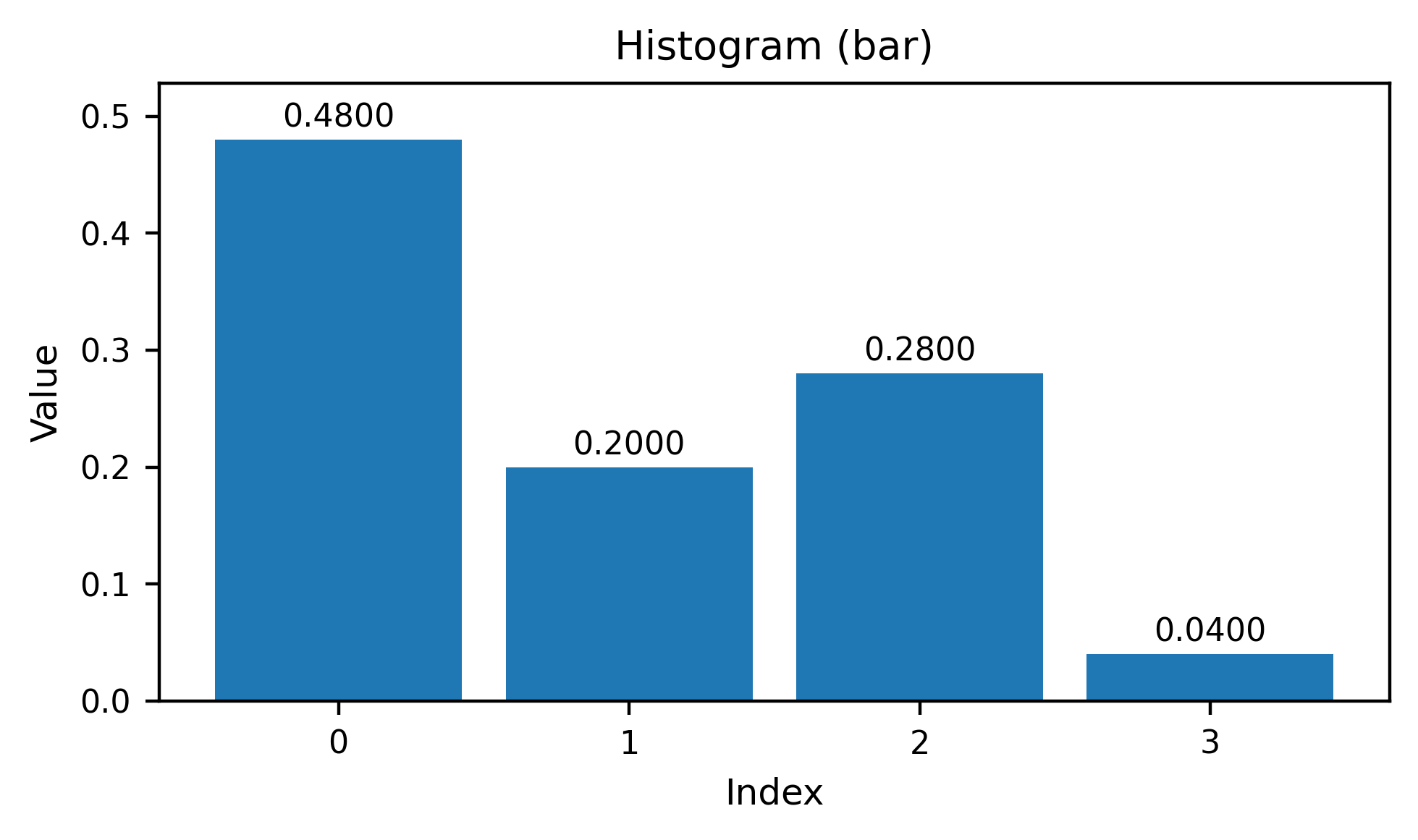
[19]:
(<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'Histogram (bar)'}, xlabel='Index', ylabel='Value'>)
[20]:
avg_angles = brep_encoder.push_average_face_pair_angle_histograms(10,4)
helper_tutorials.plot_bar(avg_angles[15,10])
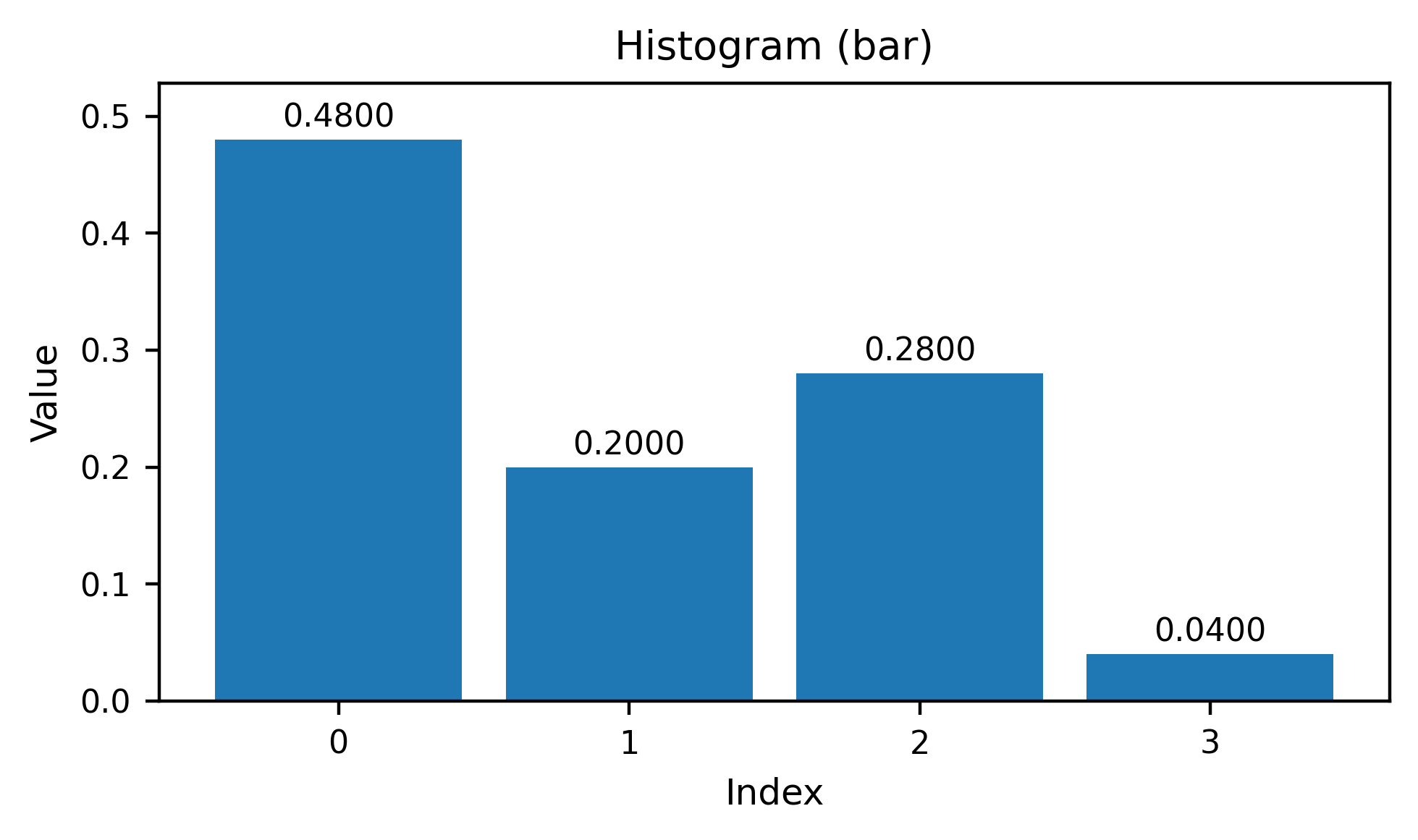
[20]:
(<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'Histogram (bar)'}, xlabel='Index', ylabel='Value'>)
Encoding the Geometry
Samples points, normals, and inside/outside information on a discretized grid across each face.
[21]:
face_discretization = brep_encoder.push_face_discretization(pointsamples=24) # 16 sample points per face
print("face_discretization\n", face_discretization.shape)
face_discretization
(21, 24, 7)
[22]:
#print(face_discretization)
[23]:
viewer.clear_face_colors()
use_face_index = 5
viewer.set_face_color([use_face_index])
helper_tutorials.plot_face_points(face_discretization, face_idx=use_face_index, show_normals=True, connect=False)
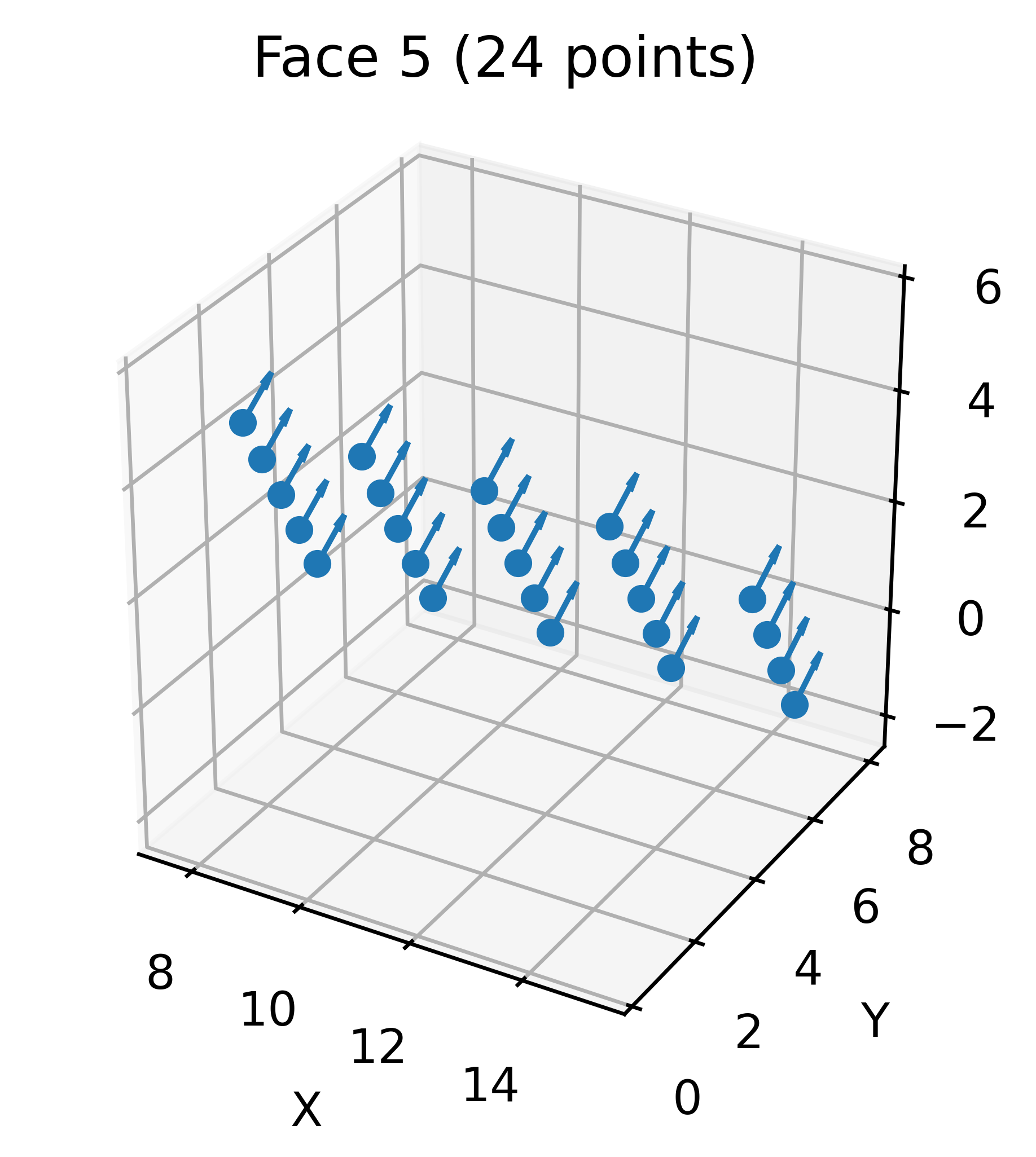
[23]:
(<Figure size 1200x900 with 1 Axes>,
<Axes3D: title={'center': 'Face 5 (24 points)'}, xlabel='X', ylabel='Y', zlabel='Z'>)
[ ]:
Samples points along edges at regular intervals.
Parameters:
ugrid: Number of sample points along each edge (default: 5)
Returns: 0 on success
Storage Format: edgecount—ugrid—feature_dim numpy array of sampled data
[24]:
edge_discretization = brep_encoder.push_curvegrid(5)
print("edge_discretization\n", edge_discretization.shape)
edge_discretization
(46, 5, 6)
Extracts and stores various face attributes, including face types, areas, and loop counts.
Encoding the attributes
[25]:
[face_types, face_areas, face_loops], face_types_descr = brep_encoder.push_face_attributes()
print("face_types", face_types)
print("face_areas", face_areas)
print("face_loops", face_loops)
print("face_types_descr", face_types_descr)
face_types [0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2]
face_areas [ 43.911655 141.3149 75.277115 51.831074 24.732485 57.030937
19.963306 12.871587 28.228918 39.265965 39.265965 12.871587
57.030937 57.030933 57.030937 57.030937 57.030933 51.831074
141.3149 10.575602 10.575602]
face_loops [2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1]
face_types_descr {0: 'Plane', 1: 'Cylinder', 2: 'Cone'}
Extracts and stores various edge attributes, including edge types, lengths, dihedral angles, and convexities.
Storage Keys: “edge_types”, “edge_lengths”, “edge_dihedral_angles”, “edge_convexities”, and metadata “descriptions/edge_types”
Storage Format: 1D numpy arrays for each attribute type
[26]:
[edge_types_np, edge_lengths_np, edge_dihedrals_np, edge_convexities_np], edge_type_descrip = brep_encoder.push_edge_attributes()
print("edge_types_np", edge_types_np)
print("edge_lengths_np", edge_lengths_np)
print("edge_dihedrals_np", edge_dihedrals_np)
print("edge_convexities_np", edge_convexities_np)
print("edge_type_descrip", edge_type_descrip)
edge_types_np [1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]
edge_lengths_np [14.137167 14.137167 7.8539815 7.8539815 18. 7.8539815
18. 17.278759 17.278759 7.8539815 3. 3.
17.278759 17.278759 5.196152 5.196152 5.196152 5.196152
5.196152 5.196152 10.97561 5.196152 10.97561 5.196152
5.196152 5.196152 5.196152 5.196152 12.566371 12.566371
1.0243902 12.566371 1.0243902 15.707963 15.707963 12.566371
2.5 2.5 15.707963 15.707963 10.97561 10.97561
10.97561 10.97561 0.70710677 0.70710677]
edge_dihedrals_np [ 7.8539819e-01 7.8539819e-01 -1.5707964e+00 -1.5707964e+00
2.4492937e-16 1.5707964e+00 0.0000000e+00 -1.5707964e+00
-1.5707964e+00 1.5707964e+00 0.0000000e+00 2.4492937e-16
1.5707964e+00 1.5707964e+00 -1.5707964e+00 -1.5707964e+00
-1.5707964e+00 -1.5707964e+00 -1.5707964e+00 -1.5707964e+00
1.0471976e+00 1.5707964e+00 1.0471976e+00 1.5707964e+00
1.5707964e+00 1.5707964e+00 1.5707964e+00 1.5707964e+00
-1.5707964e+00 -1.5707964e+00 2.4492937e-16 1.5707964e+00
0.0000000e+00 -1.5707964e+00 -1.5707964e+00 1.5707964e+00
0.0000000e+00 2.4492937e-16 7.8539819e-01 7.8539819e-01
1.0471976e+00 1.0471976e+00 1.0471976e+00 1.0471976e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00]
edge_convexities_np [1 1 2 2 3 1 3 2 2 1 3 3 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 1 3 2 2 1 3
3 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3]
edge_type_descrip {1: 'Circle', 0: 'Line'}
[ ]:
[ ]:
[27]:
viewer.terminate()
[ ]:

