Embeddings & Similarity Search
Important
Purpose: This document is for Developers and Engineers who want an overview of shape embeddings and similarity search.
For training custom models, see the Shape Embeddings Model.
For the end-to-end production workflow (embed, index, search, persist), see Similarity Search Workflow.
This page covers the core concepts and helps you choose between using a pre-trained model vs training a custom one.
Concepts
If you’re new to the topic, here are the core ideas in plain terms.
Embeddings
An embedding is a numeric representation of an object (for example a CAD part) as a fixed-length vector of numbers. The goal is that similar things end up close together in that vector space.
An embedding turns something complex (a 3D shape, text, an image) into a vector like:
[0.12, -0.03, ...].Once objects are vectors, you can compare them using distance/similarity metrics (commonly cosine similarity or Euclidean distance).
A good embedding model is trained so that “similar” in your domain corresponds to “nearby” in the embedding space.
Retrieval (Similarity Search)
Retrieval (often called vector search or similarity search) is the process of:
Creating an embedding for a query (e.g., a new CAD file)
Searching an index of existing embeddings
Returning the nearest neighbors (the most similar items)
Because datasets can be large, embeddings are typically stored in a specialized vector index (e.g., FAISS) to make nearest-neighbor search fast.
What Is a Shape Embedding?
A shape embedding is an embedding specifically for 3D geometry. In HOOPS AI, a shape embedding model maps a CAD file (STEP/IGES/etc.) into a vector such that parts with similar geometry tend to have similar vectors.
Use shape embeddings to find CAD parts that “look like” a query part.
In this guide:
HOOPSEmbeddingscomputes shape embeddings from CAD files.CADSearchindexes those vectors and performs fast retrieval.
Overview
The HOOPSEmbeddings API provides production-ready tools for:
✅ Computing embeddings from CAD files (single or batch)
✅ Vector database connectors (FAISS, with Qdrant/Weaviate/Pinecone support planned)
✅ Similarity search and retrieval in optimized vector spaces
✅ Pre-trained models ready to use out-of-the-box
✅ Custom model support via model registration
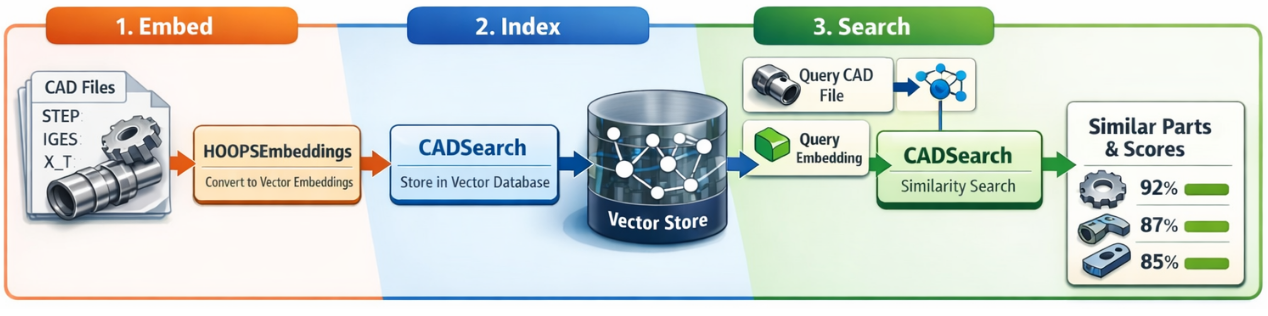
Production Workflow (3 Steps)
Embed: Convert CAD files to vector embeddings using HOOPSEmbeddings
Index: Store embeddings in a vector store using CADSearch
Search: Query for similar parts using CAD files or embeddings
When to Train Custom Models
Your CAD parts have unique geometric characteristics not captured by pre-trained models
You need domain-specific embeddings (e.g., specific industry, manufacturing process)
You have a large proprietary dataset to learn from
You want to optimize embedding dimensions for your use case
Note: HOOPS AI’s provided a pre-trained model (e.g., ts3d_scl_dual_v1) that can be used directly. See the production guide on how to use it directly. Trained on a large dataset with nearly 1M parts from public datasets (ABC, fabwave, etc).
Using Pre-trained vs Custom Models
Pre-trained Models (Recommended for most users):
# Use HOOPS AI's pre-trained model - no training required!
embedder = HOOPSEmbeddings(model="ts3d_scl_dual_v1")
Custom Trained Models (For specialized domains):
# Register your custom model (trained using EmbeddingFlowModel)
HOOPSEmbeddings.register_model(
model_name="my_custom_model",
checkpoint_path="/path/to/best.ckpt"
)
# Use your custom model
embedder = HOOPSEmbeddings(model="my_custom_model", device="cpu")
Want to train a custom model? See the Shape Embeddings Model.
For the full production workflow (embed, index, search, and persist indices), see Similarity Search Workflow.
For training custom embedding models, see Train a Shape Embedding Model.
For visualizing retrieval hits, see Search Results Visualization.

