Model
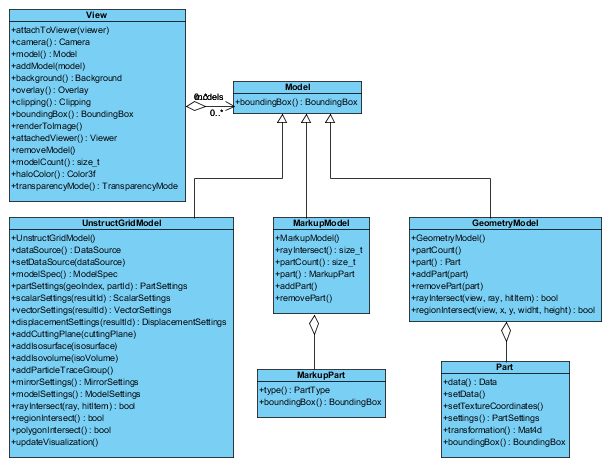
A Model is responsible for collecting the information needed to compose a view. It serves as an abstract base class, and all models are required to implement this interface.
The Model class has three main subclasses:
- UnstructGridModel
- MarkupModel
- GeometryModel
UnstructGridModel
The UnstructGridModel class is a
subclass of Model which adds specific model structure and functionality for representing
scientific and engineering models, e.g. finite element data.
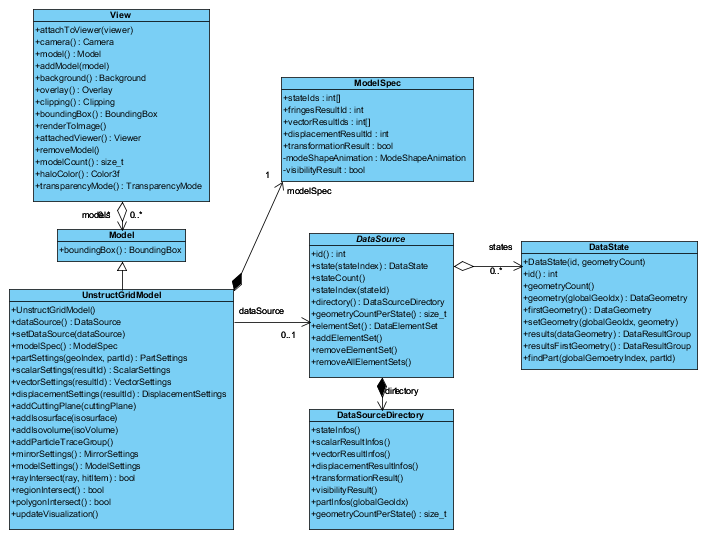
Essential to UnstructGridModel is DataSource which represents the actual source of model
information. Subclasses to DataSource distinguish between file based and programmatic input of
model information.
See topic Getting data into UnstructGridModel for further descriptions of data sources.
UnstructGridModel employs a model specification, the ModelSpec class, to specify what to
visualize at any given time. ModelSpec enables selection of states (e.g. load cases, time steps,
and frequencies), and results (scalar, vector, and displacements).
The data model consists of nodes, elements, element connectivity, and aggregations to parts.
Nodes and elements can be index- or id-based. Elements also have optional user properties.
The parts bind elements and nodes. A geometry consists of a collection of parts. The Unstructured Grid component
supports multiple geometries per state and allows combination of static and dynamic geometries. All parts
have its own part settings.
The data model may contain multiple scalar, vector results, displacement results and transformations.
The Unstructured Grid component supports partial results (results available only for a subset of parts).
See the Unstruct Grid Component documentation for further information.
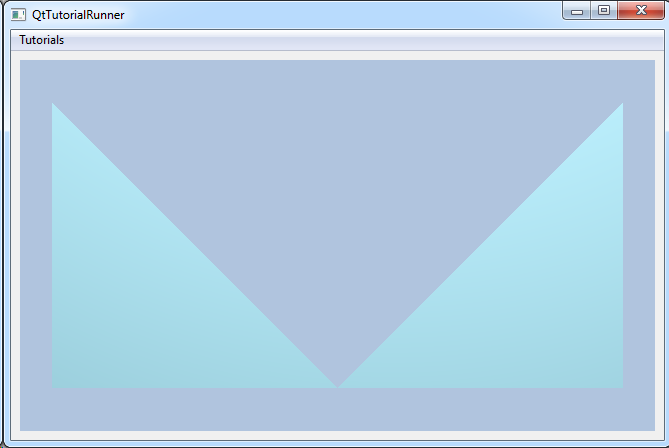 |
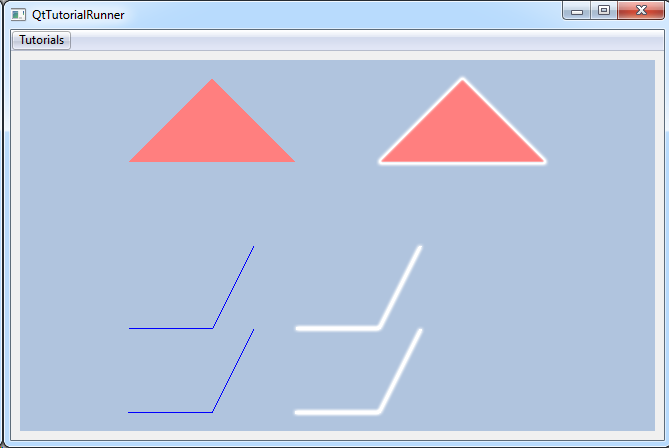
Tutorial: UnstructGrid: Simple Model with Two Triangles Shows how to create your own part and to use it in a model. The geometry is a very simple structure containing two triangles only. |
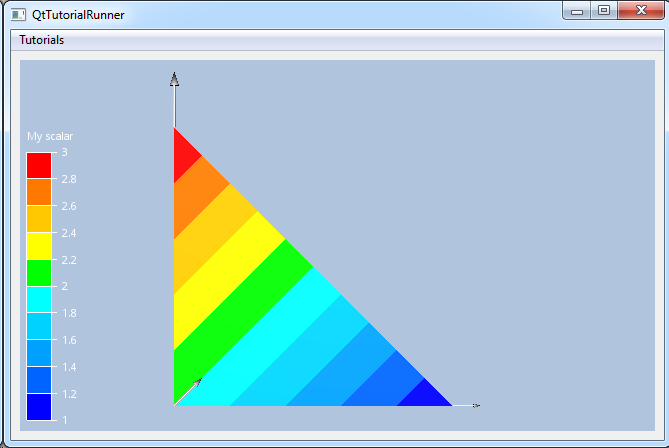 |
Tutorial: UnstructGrid: A Simple Model with Results Shows how to build an UnstructGridModel geometry, part and results. The geometry is a very simple structure containing a single triangle and a scalar result mapped as fringes, a vector result and a displacement result. |
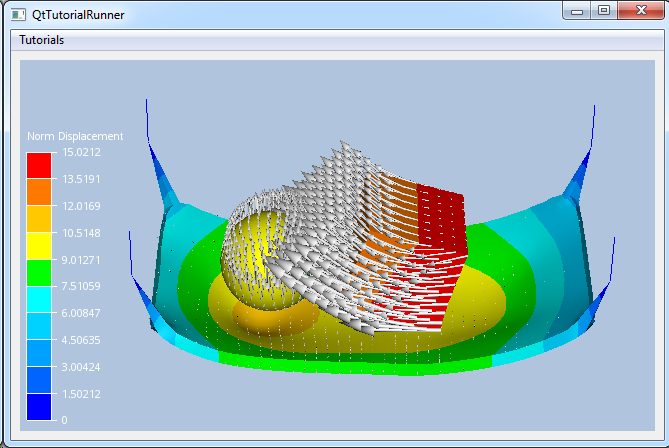 |
Tutorial: UnstructGrid: Load Model from File and Set Up Model Specification Shows how to create a data source by loading a VTFx file and how to setup a model specification. |
MarkupModel
The cee::vis::MarkupModel class is a subclass of cee::vis::Model which
draws simple object and markups such as annotations, distance measurements etc.
The following markup part types are available:
LabelsTrianglesLinesPointsArrowsFixed size arrowFixed size glyphFixed size spheresText 3DInstanced geometry
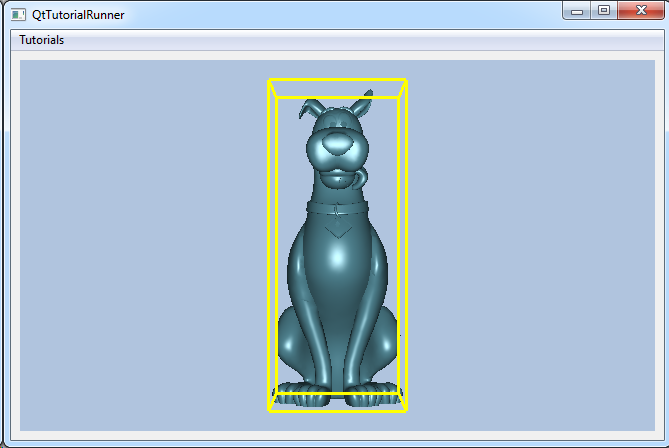 |
Tutorial: Visualization: Draw Bounding Box Using Markup Model Shows how to create a data source by loading a VTFx file and drawing the models bounding box as a markup model. |
GeometryModel
The GeometryModel class is a subclass of Model which
can handle a large number of Parts efficiently.
It supports the following part types:
Each part has with relevant effects/attributes like color, textures, opacity/transparency, size/width, halo/silhouetted edges, lighting etc.
The GeometryModel supports ray and region intersects which may be used to mimic e.g. picking/selection schemes.
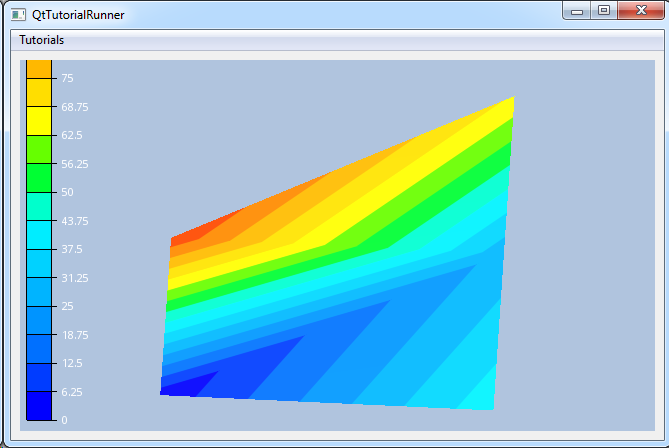
 |
Tutorial: Geometry: Create a Geometry Model Shows how to create a geometry model with different parts and effects. |
 |
Tutorial: Geometry: Create a Geometry Model with Texture Shows how to create a geometry model using the texture effect to show a scalar result. |
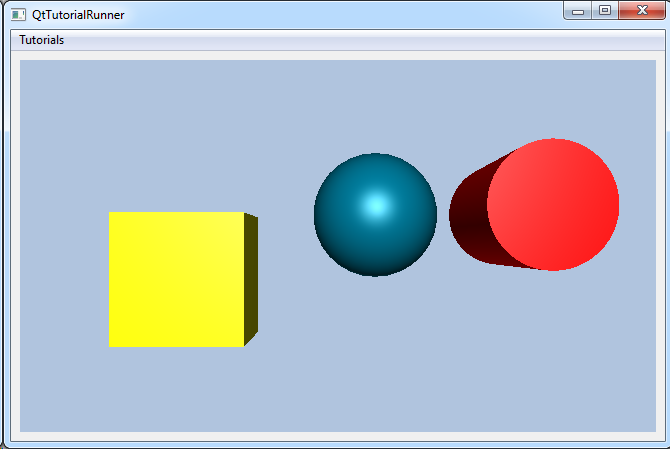 |
Tutorial: Geometry: Create a Geometry Model with Geometric Primitives Shows how to create a geometry with geometric primitives like spheres, boxes and cylinders. |

