Using the Realistic Material
HOOPS Luminate provides an all-purpose, realistic material. This material is energetically equilibrated and fully customizable. Using that material, you should be able to reproduce the look & feel of almost every material in nature.
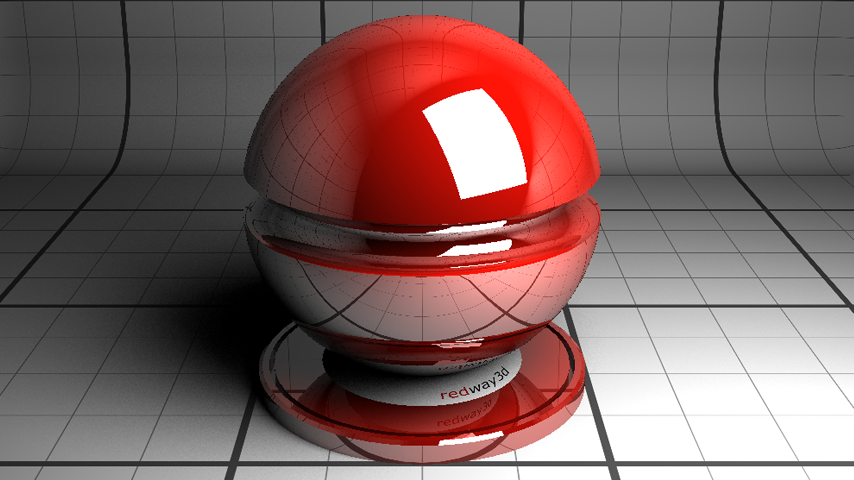

The default realistic material
Creating a Realistic Material
Call RED::IMaterial::SetupRealisticMaterial to setup a realistic material from an existing material object. The creation of a material occurs using RED::IResourceManager::CreateMaterial.
Realistic materials can also be created Using HOOPS Luminate’s Material Editor. In this case, materials are saved to .red files and can be reloaded like any other material. See Loading a Material from Library for details on these operations.
The Realistic Material Shading Model
The realistic material shading model uses several basic inputs, that are summarized below:
| Input | Description | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| Diffusion | This is the diffuse color / texture information of the material, used in a Lambertian equation. | 
|
| Transmission | This is the transmission color / texture information of the material. The transmission has precedence over the diffusion term for the calculation of energy preservation. | 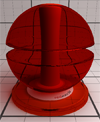
|
| Reflection | This is the reflection color / texture information of the material. The reflection has precedence over the diffusion and transparency terms for the calculation of energy preservation. | 
|
These three inputs are all involved in the energy preservation rule which is enforced by the realistic material shading model: the sum of the diffusion + reflection + transmission terms is always lower than or equal to 1.0. This is summarized below:
reflect' = reflect // reflection color is the dominant color and we left it unmodified
transmission' = (white - reflect') * transmission
diffuse' = (white - reflect' - transmission') * diffuse
This means that a realistic material with a reflection color set to white is totally opaque and reflective, even if any of the other components is not black.
Then, these inputs can be modified using special parameters:
| Input | Description | Sample |
|---|---|---|
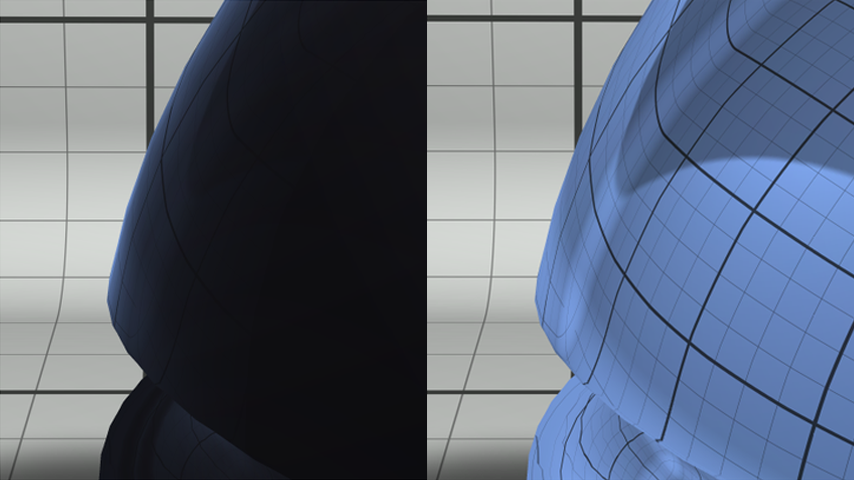
| Fresnel | The fresnel option is a very powerful term that is used to modulate the amount of reflection emitted by the material based on the angle of the viewing direction with the surface. This must be turned on for all glasses materials. | ..image:: bk_bm_realistic_fresnel.png |
| Anisotropic Reflectance | This is an extra anisotropic term that can be set to specify anisotropic reflections in the realistic material. Two anisotropy values (anisotropy in U and anisotropy in V) can be set, or texture with at least two channels (red and green) can be set instead, to define a per-pixel anisotropic information. Anisotropy values are in [0.0f, 1.0f]. The larger the value the wider the reflection angle. | 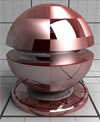
|
| Anisotropy Orientation | This term defines the orientation of the anisotropy. Either a single angular value or a texture with at least one channel (red) defines the value of the rotation angle to apply to the basis used to define the reflectance of the material. Angles are expressed in radians. The read texture value is multiplied by 2*PI to map the usual [0.0,1.0] range to [0.0,2*PI]. | 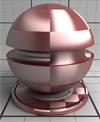
|
| Transmission Glossiness | This term defines the glossiness value of the material. A single glossiness value or a texture with at least one channel (red) can be used to define the per-pixel transmission glossiness of the material. Glossiness values are in [0.0f,1.0f]. The larger the value the wider the transmission glossiness cone. | 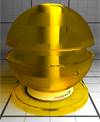
|
| Transmission Scattering | This is an extra absorption term that can be specified for the material transmission. It uses an out-scattering color and an out-scattering scale used to specifiy the amount of energy being absorbed along the path of a ray for each unit length crossed in the model media volume. This is related to \ref bk_re_sw3d_volume. | 
|
| Reflection Fog | This is fade-out term that can be specified for reflections. At a certain distance, the color of the reflection becomes equal to the specified reflection fog color, and any other visible reflection is lost. | 
|
Finally, the realistic material also features surface modifiers, that are detailed below:
| Input | Description | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| Bump Map | The bump map of the realistic material affects the surface normal of the geometry at the shaded fragment. | 
|
| Displacement Map | The displacement map of the realistic material modifies the surface of the geometry that uses it. See Displacement | 
|
Diffusion
The diffusion model used is Lambertian, meaning that the incoming light is diffused uniformly in every outgoing direction (i.e. in the whole hemisphere around the surface hit point). It is controlled giving one color (constant over the surface or by texel using a texture). A light that illuminates a surface produces a more visible lighting if it’s aligned with the surface normal. .. note:
According to the previously detailed energy preservation rule, the object may appear of another color than the diffuse one if reflection and / or transmission are used.
Reflection
In our realistic material, reflections have greater weight than two others shading components. First, the user has to choose between two different behaviors (see the figure below):
- Fresnel-like reflections: the reflection amount is proportional to the opposite of the dot product between the eye vector and the surface normal. Reflections are then stronger near the grazing angles. We use the Schlick Fresnel term approximation in our model (as in almost any other shading models found in the literature). Note that the reflection amount is still post-multiplied by the user-given reflection color.
- Uniform reflection: the reflection amount is read from the material input (constant color or texture)
Fresnel reflections (on the left) compared to uniform ones (on the right); in the Fresnel case, note how the reflection fades off as the angle between the eye vector and the surface normal decreases
Whatever the model you choose, reflections can be made glossy and / or anisotropic. The glossiness is a measure of the dispersion of the reflection rays around the perfectly specular reflection vector. It can be seen as the half-angle of the cone subtended by the reflection vector where reflection samples are taken. The more the angle increases the more the reflections are blurry (and will require samples to avoid too much noise; see figure below).
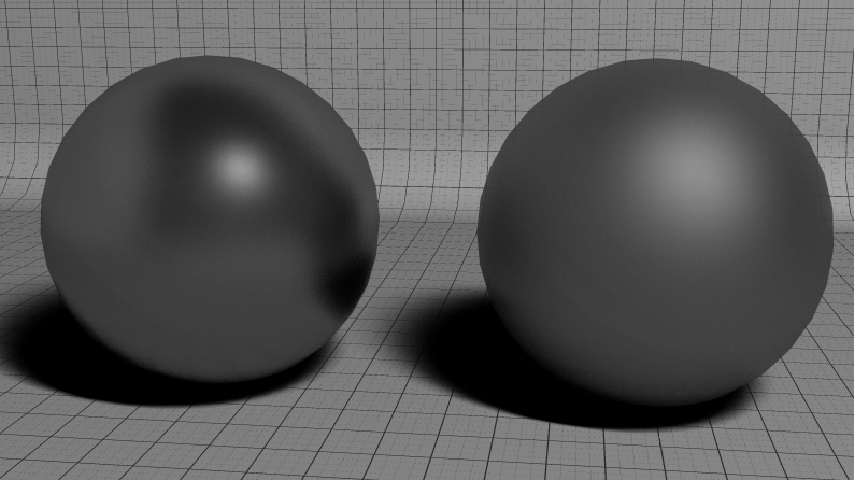
The sphere on the left is less glossy than the one on the right.
The anisotropy defines the shape of the reflections. Anisotropic materials reflect light according to the surface orientation (see figure below). It means that a local surface coordinate system is needed to handle oriented reflections. The basis used is the one given by the normal and the tangent vectors to the surface (see RED::IMeshShape::BuildTangents).
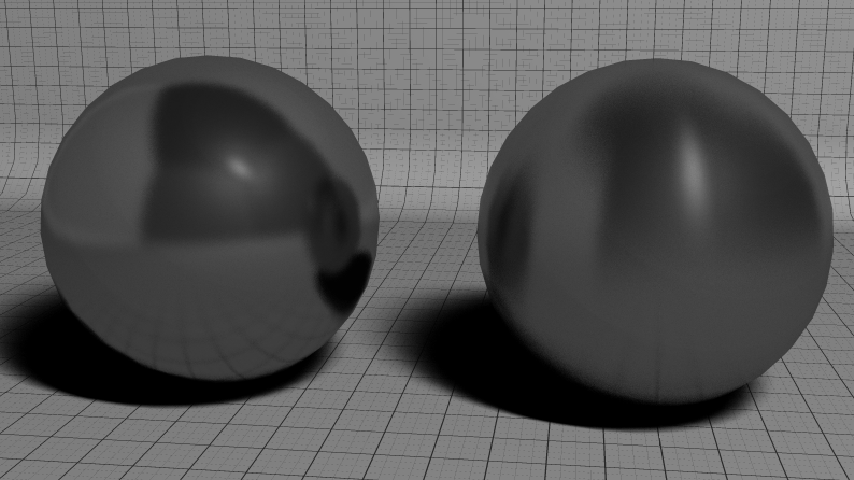
The sphere on the left is isotropic as the one on the right is anisotropic. Notice how reflections are vertically distorted in the anisotropic case
Transmission
Every realistic material has its own index of refraction (IOR; see the Table of common IOR (Table of Common Indices of Refraction) for a list of known material IOR). When transparent, the material IOR is used to deviate light rays when they travel through the volume (see figure below).
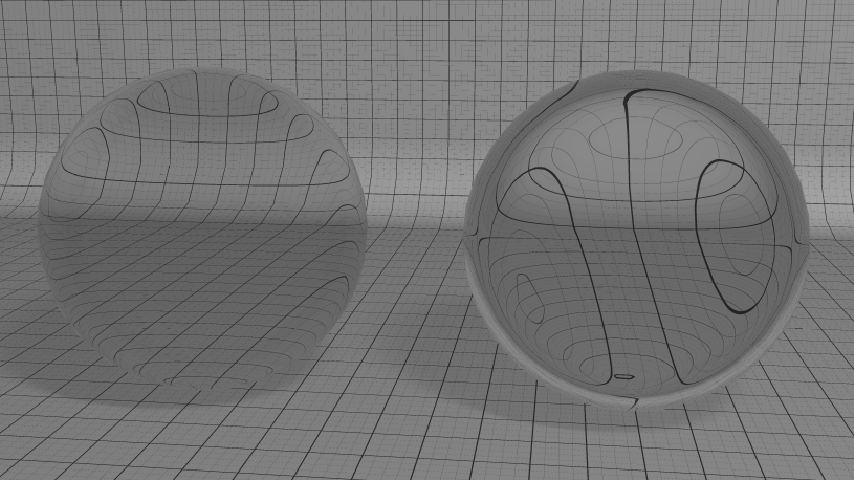
The same realistic material with two different IOR values (1.02 on the left and 1.1 on the right)
As for reflections, refractions can be glossy to simulate a wide range of materials:
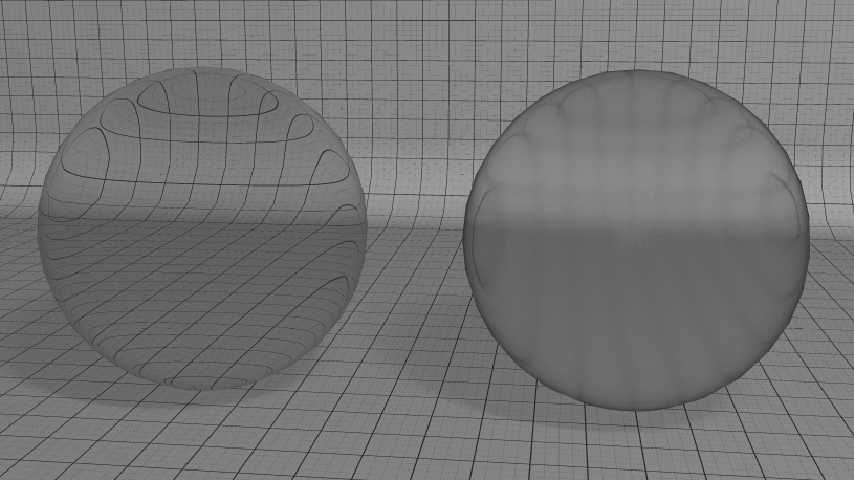
The same realistic material with (on the right) or without (on the left) refraction glossiness
GPU Rendering
The rendering of the realistic material on the GPU is quite slow due to the complexity of the parameters it handles. Most parameters are properly supported on the GPU except the transmission glossiness texture and the reflection glossiness texture that are both ignored if the material is rendered using a GPU.
Real-Time vs. Photo-Realistic Configurations
The realistic material can be created for real-time rendering needs or for photo-realistic rendering needs, or for both needs, when using RED::IMaterial::SetupRealisticMaterial. The real-time version of the realistic material will use environmental mapping techniques instead of true ray-traced reflections. It’ll also use refraction effects instead of true refractions, to ensure it can be rendered at real-time rates.
Realistic Material Properties
A realistic material is setup with a built-in material controller linked with it. Here is the full list of the realistic material properties. Each time a property name uses the ‘+’ term, this means that the two strings indicated by #define statements must be concatenated.
Properties names are listed below:
| Property | Type | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffuse Component | |||
RED_MATCTRL_DIFFUSE_COLOR |
Color | n/a | Color used for diffusion |
RED_MATCTRL_DIFFUSE_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Texture used for diffusion |
RED_MATCTRL_DIFFUSE_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Diffuse texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_DIFFUSE_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Diffuse texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_DIFFUSE_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Diffuse texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_DIFFUSE_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Diffuse texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_DIFFUSE_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Diffuse texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_DIFFUSE_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for diffuse texture uv coordinates |
| Transmission Component | |||
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_COLOR |
Color | n/a | Color used for transmission |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Texture used for transmission |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for transmission texture uv coordinates |
| Transmission Glossiness Component | |||
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_GLOSSINESS_ANGLE |
Float | [0.0f,+inf[ | Transmission glossiness angle |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_GLOSSINESS_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Texture used for transmission glossiness. The first channel of the texture is used. |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_GLOSSINESS_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_GLOSSINESS_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_GLOSSINESS_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_GLOSSINESS_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_GLOSSINESS_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Transmission texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_GLOSSINESS_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for transmission glossiness texture uv coordinates |
| Bump Component | |||
RED_MATCTRL_BUMP_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Texture used for bump |
RED_MATCTRL_BUMP_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Bump texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_BUMP_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Bump texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_BUMP_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Bump texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_BUMP_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Bump texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_BUMP_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Bump texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_BUMP_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for bump texture uv coordinates |
RED_MATCTRL_TANGENTS_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for tangent vectors definition |
| Environment Component (Real-Time Realistic Materials) | |||
RED_MATCTRL_ENVIRONMENT_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Texture used for environment mapping |
RED_MATCTRL_ENVIRONMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Environment texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ENVIRONMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Environment texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ENVIRONMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Environment texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ENVIRONMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Environment texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ENVIRONMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Environment texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_ENVIRONMENT_AUTO |
Boolean | [false, true] | Toggle automatic environment maps (generated using RED::RenderShaderParameter::REF_AUTO_CUBE_MAP) |
RED_MATCTRL_ENVIRONMENT_BACK |
Boolean | [false, true] | Toggle background environment maps (from RED::IViewpointRenderList::SetBackgroundImages) |
| Reflection Component | |||
RED_MATCTRL_REFLECTION_COLOR |
Color | n/a | Color used for reflection |
RED_MATCTRL_REFLECTION_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Texture used for reflection |
RED_MATCTRL_REFLECTION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Reflection texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_REFLECTION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Reflection texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_REFLECTION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Reflection texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_REFLECTION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Reflection texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_REFLECTION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Reflection texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_REFLECTION_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for reflection texture uv coordinates |
| Anisotropy Component | |||
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_U |
Float | [0.0f,+inf[ | Anisotropy along the U axis of the local (tangent, binormal, normal) basis at the shaded fragment |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_V |
Float | [0.0f,+inf[ | Anisotropy along the V axis of the local (tangent, binormal, normal) basis at the shaded fragment |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Texture used for the reflection anisotropy |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for anisotropy texture uv coordinates |
| Anisotropy Rotation Component | |||
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_ROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy rotation angle around the normal axis of the local (tangent, binormal, normal) basis at the shaded fragment |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_ROTATION_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Texture used for the rotation of the anisotropy |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_ROTATION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy rotation texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_ROTATION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy rotation texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_ROTATION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy rotation texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_ROTATION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy rotation texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_ROTATION_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Anisotropy rotation texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_ANISOTROPY_ROTATION_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for anisotropy rotation texture uv coordinates |
| Displacement Component | |||
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_HEIGHT |
Float | ]0.0f,+inf[ | Height amplitude of the surface displacement, in model units |
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_OFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Offset applied to the height ampliture of the surface displacement, in model units |
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_TEXTURE |
Texture | n/a | Displacement map texture |
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Displacement texture translation along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VOFFSET |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Displacement texture translation along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_USCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Displacement texture repetition along the u axis |
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_VSCALE |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Displacement texture repetition along the v axis |
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_MATRIX + RED_MATCTRL_UVMATRIX_UVROTATION |
Float | ]-inf,+inf[ | Displacement texture rotation along the normal to the surface |
RED_MATCTRL_DISPLACEMENT_CHANNEL |
Integer | [0, 15] | Mesh input channel for displacement texture uv coordinates |
| Miscellaneous Properties | |||
RED_MATCTRL_DOUBLESIDED |
Boolean | [false,true] | Is the material double sided? |
RED_MATCTRL_FRESNEL |
Boolean | [false,true] | Is the material using a Fresnel reflectance model? |
RED_MATCTRL_IOR |
Float | ]0.0f,+inf[ | Index Of Refraction (IOR) of the material |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_SCATTERING_COLOR |
Color | n/a | Color used for the material transmission scattering |
RED_MATCTRL_TRANSMISSION_SCATTERING_SCALE |
Float | ]0.0f,+inf[ | Model unit scaling applied to the transmission scattering distance |
RED_MATCTRL_CAUSTICS_REFLECTIVE |
Boolean | [false,true] | Is the material emitting reflective caustics? |
RED_MATCTRL_CAUSTICS_REFRACTIVE |
Boolean | [false,true] | Is the material emitting refractive caustics? |
Table of Common Indices of Refraction
| Material | IOR |
|---|---|
| Acetone | 1.36 |
| Air | 1.0 |
| Alcohol | 1.33 |
| Chromium Oxide | 2.7 |
| Copper Oxyde | 2.7 |
| Crystal | 2.0 |
| Diamond | 2.42 |
| Emerald | 1.57 |
| Ethyl Alcohol | 1.36 |
| Glass | 1.5 |
| Glass, Crown | 1.52 |
| Glass, Heaviest Flint | 1.89 |
| Glass, Heavy Flint | 1.65 |
| Glass, Light Flint | 1.57 |
| Glass, Zinc Crown | 1.52 |
| Ice | 1.31 |
| Iodine Crystal | 3.34 |
| Lapis Lazuli | 1.61 |
| Polystyrene | 1.55 |
| Pyrex | 1.47 |
| Quartz | 1.6 |
| Quartz, Fused | 1.46 |
| Ruby | 1.77 |
| Sapphire | 1.77 |
| Silicon | 4.01 |
| Topaz | 1.61 |
| Water | 1.33 |
